电商购物网站开发东莞今日头条新闻
java线程池动态调节功能实现
- 功能背景
- ThreadPoolExecutor配置
- 自定义可变容LinkedBlockingQueue
- controller接口
- 测试结果
功能背景
由于线程池的参数配置是一个比较难准确配置好, 如果需要进行配置修改, 就会对配置进行修改,再进行部署,影响效率, 或者应用场景的变化,导致固定的配置很难满足当前需求, 需要对线程池的参数进行动态配置, 查找资料发现很多博客在说美团发布的一篇文字《Java线程池实现原理及其在美团业务中的实践》, 于是手进行实现
ThreadPoolExecutor配置
mport io.micrometer.core.instrument.util.NamedThreadFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;/*** desc: 线程池配置** @author qts* @date 2023/11/15 0015*/
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {@Beanpublic ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor() {return new ThreadPoolExecutor(2,4,60, TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<>(10),new NamedThreadFactory("my-executor"),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());//拒绝策略:当前调用线程进行执行}}
自定义可变容LinkedBlockingQueue
由于LinkedBlockingQueue中的capacity被 final修饰,无法进行修改, 故将LinkedBlockingQueue代码复制,后将capacity的final删除,并提getter和setter方法, 代码如下
/** ORACLE PROPRIETARY/CONFIDENTIAL. Use is subject to license terms.*//** Written by Doug Lea with assistance from members of JCP JSR-166* Expert Group and released to the public domain, as explained at* http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/*/import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.function.Consumer;/*** An optionally-bounded {@linkplain BlockingQueue blocking queue} based on* linked nodes.* This queue orders elements FIFO (first-in-first-out).* The <em>head</em> of the queue is that element that has been on the* queue the longest time.* The <em>tail</em> of the queue is that element that has been on the* queue the shortest time. New elements* are inserted at the tail of the queue, and the queue retrieval* operations obtain elements at the head of the queue.* Linked queues typically have higher throughput than array-based queues but* less predictable performance in most concurrent applications.** <p>The optional capacity bound constructor argument serves as a* way to prevent excessive queue expansion. The capacity, if unspecified,* is equal to {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}. Linked nodes are* dynamically created upon each insertion unless this would bring the* queue above capacity.** <p>This class and its iterator implement all of the* <em>optional</em> methods of the {@link Collection} and {@link* Iterator} interfaces.** <p>This class is a member of the* <a href="{@docRoot}/../technotes/guides/collections/index.html">* Java Collections Framework</a>.** @since 1.5* @author Doug Lea* @param <E> the type of elements held in this collection*/
public class ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6903933977591709194L;/** A variant of the "two lock queue" algorithm. The putLock gates* entry to put (and offer), and has an associated condition for* waiting puts. Similarly for the takeLock. The "count" field* that they both rely on is maintained as an atomic to avoid* needing to get both locks in most cases. Also, to minimize need* for puts to get takeLock and vice-versa, cascading notifies are* used. When a put notices that it has enabled at least one take,* it signals taker. That taker in turn signals others if more* items have been entered since the signal. And symmetrically for* takes signalling puts. Operations such as remove(Object) and* iterators acquire both locks.** Visibility between writers and readers is provided as follows:** Whenever an element is enqueued, the putLock is acquired and* count updated. A subsequent reader guarantees visibility to the* enqueued Node by either acquiring the putLock (via fullyLock)* or by acquiring the takeLock, and then reading n = count.get();* this gives visibility to the first n items.** To implement weakly consistent iterators, it appears we need to* keep all Nodes GC-reachable from a predecessor dequeued Node.* That would cause two problems:* - allow a rogue Iterator to cause unbounded memory retention* - cause cross-generational linking of old Nodes to new Nodes if* a Node was tenured while live, which generational GCs have a* hard time dealing with, causing repeated major collections.* However, only non-deleted Nodes need to be reachable from* dequeued Nodes, and reachability does not necessarily have to* be of the kind understood by the GC. We use the trick of* linking a Node that has just been dequeued to itself. Such a* self-link implicitly means to advance to head.next.*//*** Linked list node class*/static class Node<E> {E item;/*** One of:* - the real successor Node* - this Node, meaning the successor is head.next* - null, meaning there is no successor (this is the last node)*/ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> next;Node(E x) { item = x; }}/** The capacity bound, or Integer.MAX_VALUE if none */private int capacity;/** Current number of elements */private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();/*** Head of linked list.* Invariant: head.item == null*/transient ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> head;/*** Tail of linked list.* Invariant: last.next == null*/private transient ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> last;/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();/** Wait queue for waiting takes */private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();/** Wait queue for waiting puts */private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();/*** Signals a waiting take. Called only from put/offer (which do not* otherwise ordinarily lock takeLock.)*/private void signalNotEmpty() {final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lock();try {notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}}/*** Signals a waiting put. Called only from take/poll.*/private void signalNotFull() {final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;putLock.lock();try {notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}}/*** Links node at end of queue.** @param node the node*/private void enqueue(ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> node) {// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert last.next == null;last = last.next = node;}/*** Removes a node from head of queue.** @return the node*/private E dequeue() {// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert head.item == null;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> h = head;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> first = h.next;h.next = h; // help GChead = first;E x = first.item;first.item = null;return x;}/*** Locks to prevent both puts and takes.*/void fullyLock() {putLock.lock();takeLock.lock();}/*** Unlocks to allow both puts and takes.*/void fullyUnlock() {takeLock.unlock();putLock.unlock();}// /**
// * Tells whether both locks are held by current thread.
// */
// boolean isFullyLocked() {
// return (putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread() &&
// takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread());
// }/*** Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}.*/public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue() {this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);}/*** Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue} with the given (fixed) capacity.** @param capacity the capacity of this queue* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code capacity} is not greater* than zero*/public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();this.capacity = capacity;last = head = new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(null);}/*** Creates a {@code ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue} with a capacity of* {@link Integer#MAX_VALUE}, initially containing the elements of the* given collection,* added in traversal order of the collection's iterator.** @param c the collection of elements to initially contain* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection or any* of its elements are null*/public ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibilitytry {int n = 0;for (E e : c) {if (e == null)throw new NullPointerException();if (n == capacity)throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");enqueue(new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(e));++n;}count.set(n);} finally {putLock.unlock();}}// this doc comment is overridden to remove the reference to collections// greater in size than Integer.MAX_VALUE/*** Returns the number of elements in this queue.** @return the number of elements in this queue*/public int size() {return count.get();}// this doc comment is a modified copy of the inherited doc comment,// without the reference to unlimited queues./*** Returns the number of additional elements that this queue can ideally* (in the absence of memory or resource constraints) accept without* blocking. This is always equal to the initial capacity of this queue* less the current {@code size} of this queue.** <p>Note that you <em>cannot</em> always tell if an attempt to insert* an element will succeed by inspecting {@code remainingCapacity}* because it may be the case that another thread is about to* insert or remove an element.*/public int remainingCapacity() {return capacity - count.get();}/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if* necessary for space to become available.** @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}*/public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset local var// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.int c = -1;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> node = new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(e);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;putLock.lockInterruptibly();try {/** Note that count is used in wait guard even though it is* not protected by lock. This works because count can* only decrease at this point (all other puts are shut* out by lock), and we (or some other waiting put) are* signalled if it ever changes from capacity. Similarly* for all other uses of count in other wait guards.*/while (count.get() == capacity) {notFull.await();}enqueue(node);c = count.getAndIncrement();if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();}/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue, waiting if* necessary up to the specified wait time for space to become available.** @return {@code true} if successful, or {@code false} if* the specified waiting time elapses before space is available* @throws InterruptedException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}*/public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);int c = -1;final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;putLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == capacity) {if (nanos <= 0)return false;nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);}enqueue(new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(e));c = count.getAndIncrement();if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();return true;}/*** Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue if it is* possible to do so immediately without exceeding the queue's capacity,* returning {@code true} upon success and {@code false} if this queue* is full.* When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally* preferable to method {@link BlockingQueue#add add}, which can fail to* insert an element only by throwing an exception.** @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null*/public boolean offer(E e) {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();final AtomicInteger count = this.count;if (count.get() == capacity)return false;int c = -1;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> node = new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(e);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;putLock.lock();try {if (count.get() < capacity) {enqueue(node);c = count.getAndIncrement();if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();}} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();return c >= 0;}public E take() throws InterruptedException {E x;int c = -1;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == 0) {notEmpty.await();}x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;}public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {E x = null;int c = -1;long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);final AtomicInteger count = this.count;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == 0) {if (nanos <= 0)return null;nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);}x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;}public E poll() {final AtomicInteger count = this.count;if (count.get() == 0)return null;E x = null;int c = -1;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lock();try {if (count.get() > 0) {x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();}} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;}public E peek() {if (count.get() == 0)return null;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lock();try {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> first = head.next;if (first == null)return null;elsereturn first.item;} finally {takeLock.unlock();}}/*** Unlinks interior Node p with predecessor trail.*/void unlink(ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p, ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> trail) {// assert isFullyLocked();// p.next is not changed, to allow iterators that are// traversing p to maintain their weak-consistency guarantee.p.item = null;trail.next = p.next;if (last == p)last = trail;if (count.getAndDecrement() == capacity)notFull.signal();}/*** Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue,* if it is present. More formally, removes an element {@code e} such* that {@code o.equals(e)}, if this queue contains one or more such* elements.* Returns {@code true} if this queue contained the specified element* (or equivalently, if this queue changed as a result of the call).** @param o element to be removed from this queue, if present* @return {@code true} if this queue changed as a result of the call*/public boolean remove(Object o) {if (o == null) return false;fullyLock();try {for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;p != null;trail = p, p = p.next) {if (o.equals(p.item)) {unlink(p, trail);return true;}}return false;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** Returns {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element.* More formally, returns {@code true} if and only if this queue contains* at least one element {@code e} such that {@code o.equals(e)}.** @param o object to be checked for containment in this queue* @return {@code true} if this queue contains the specified element*/public boolean contains(Object o) {if (o == null) return false;fullyLock();try {for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)if (o.equals(p.item))return true;return false;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in* proper sequence.** <p>The returned array will be "safe" in that no references to it are* maintained by this queue. (In other words, this method must allocate* a new array). The caller is thus free to modify the returned array.** <p>This method acts as bridge between array-based and collection-based* APIs.** @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue*/public Object[] toArray() {fullyLock();try {int size = count.get();Object[] a = new Object[size];int k = 0;for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)a[k++] = p.item;return a;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue, in* proper sequence; the runtime type of the returned array is that of* the specified array. If the queue fits in the specified array, it* is returned therein. Otherwise, a new array is allocated with the* runtime type of the specified array and the size of this queue.** <p>If this queue fits in the specified array with room to spare* (i.e., the array has more elements than this queue), the element in* the array immediately following the end of the queue is set to* {@code null}.** <p>Like the {@link #toArray()} method, this method acts as bridge between* array-based and collection-based APIs. Further, this method allows* precise control over the runtime type of the output array, and may,* under certain circumstances, be used to save allocation costs.** <p>Suppose {@code x} is a queue known to contain only strings.* The following code can be used to dump the queue into a newly* allocated array of {@code String}:** <pre> {@code String[] y = x.toArray(new String[0]);}</pre>** Note that {@code toArray(new Object[0])} is identical in function to* {@code toArray()}.** @param a the array into which the elements of the queue are to* be stored, if it is big enough; otherwise, a new array of the* same runtime type is allocated for this purpose* @return an array containing all of the elements in this queue* @throws ArrayStoreException if the runtime type of the specified array* is not a supertype of the runtime type of every element in* this queue* @throws NullPointerException if the specified array is null*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {fullyLock();try {int size = count.get();if (a.length < size)a = (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);int k = 0;for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)a[k++] = (T)p.item;if (a.length > k)a[k] = null;return a;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}public String toString() {fullyLock();try {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = head.next;if (p == null)return "[]";StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();sb.append('[');for (;;) {E e = p.item;sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);p = p.next;if (p == null)return sb.append(']').toString();sb.append(',').append(' ');}} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** Atomically removes all of the elements from this queue.* The queue will be empty after this call returns.*/public void clear() {fullyLock();try {for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p, h = head; (p = h.next) != null; h = p) {h.next = h;p.item = null;}head = last;// assert head.item == null && head.next == null;if (count.getAndSet(0) == capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}*/public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);}/*** @throws UnsupportedOperationException {@inheritDoc}* @throws ClassCastException {@inheritDoc}* @throws NullPointerException {@inheritDoc}* @throws IllegalArgumentException {@inheritDoc}*/public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {if (c == null)throw new NullPointerException();if (c == this)throw new IllegalArgumentException();if (maxElements <= 0)return 0;boolean signalNotFull = false;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lock();try {int n = Math.min(maxElements, count.get());// count.get provides visibility to first n NodesResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> h = head;int i = 0;try {while (i < n) {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = h.next;c.add(p.item);p.item = null;h.next = h;h = p;++i;}return n;} finally {// Restore invariants even if c.add() threwif (i > 0) {// assert h.item == null;head = h;signalNotFull = (count.getAndAdd(-i) == capacity);}}} finally {takeLock.unlock();if (signalNotFull)signalNotFull();}}/*** Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence.* The elements will be returned in order from first (head) to last (tail).** <p>The returned iterator is* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.** @return an iterator over the elements in this queue in proper sequence*/public Iterator<E> iterator() {return new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Itr();}private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {/** Basic weakly-consistent iterator. At all times hold the next* item to hand out so that if hasNext() reports true, we will* still have it to return even if lost race with a take etc.*/private ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> current;private ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> lastRet;private E currentElement;Itr() {fullyLock();try {current = head.next;if (current != null)currentElement = current.item;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}public boolean hasNext() {return current != null;}/*** Returns the next live successor of p, or null if no such.** Unlike other traversal methods, iterators need to handle both:* - dequeued nodes (p.next == p)* - (possibly multiple) interior removed nodes (p.item == null)*/private ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> nextNode(ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p) {for (;;) {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> s = p.next;if (s == p)return head.next;if (s == null || s.item != null)return s;p = s;}}public E next() {fullyLock();try {if (current == null)throw new NoSuchElementException();E x = currentElement;lastRet = current;current = nextNode(current);currentElement = (current == null) ? null : current.item;return x;} finally {fullyUnlock();}}public void remove() {if (lastRet == null)throw new IllegalStateException();fullyLock();try {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> node = lastRet;lastRet = null;for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;p != null;trail = p, p = p.next) {if (p == node) {unlink(p, trail);break;}}} finally {fullyUnlock();}}}/** A customized variant of Spliterators.IteratorSpliterator */static final class LBQSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> current; // current node; null until initializedint batch; // batch size for splitsboolean exhausted; // true when no more nodeslong est; // size estimateLBQSpliterator(ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue) {this.queue = queue;this.est = queue.size();}public long estimateSize() { return est; }public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> h;final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;int b = batch;int n = (b <= 0) ? 1 : (b >= MAX_BATCH) ? MAX_BATCH : b + 1;if (!exhausted &&((h = current) != null || (h = q.head.next) != null) &&h.next != null) {Object[] a = new Object[n];int i = 0;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = current;q.fullyLock();try {if (p != null || (p = q.head.next) != null) {do {if ((a[i] = p.item) != null)++i;} while ((p = p.next) != null && i < n);}} finally {q.fullyUnlock();}if ((current = p) == null) {est = 0L;exhausted = true;}else if ((est -= i) < 0L)est = 0L;if (i > 0) {batch = i;return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, i, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |Spliterator.CONCURRENT);}}return null;}public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;if (!exhausted) {exhausted = true;ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = current;do {E e = null;q.fullyLock();try {if (p == null)p = q.head.next;while (p != null) {e = p.item;p = p.next;if (e != null)break;}} finally {q.fullyUnlock();}if (e != null)action.accept(e);} while (p != null);}}public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {if (action == null) throw new NullPointerException();final ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;if (!exhausted) {E e = null;q.fullyLock();try {if (current == null)current = q.head.next;while (current != null) {e = current.item;current = current.next;if (e != null)break;}} finally {q.fullyUnlock();}if (current == null)exhausted = true;if (e != null) {action.accept(e);return true;}}return false;}public int characteristics() {return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |Spliterator.CONCURRENT;}}/*** Returns a {@link Spliterator} over the elements in this queue.** <p>The returned spliterator is* <a href="package-summary.html#Weakly"><i>weakly consistent</i></a>.** <p>The {@code Spliterator} reports {@link Spliterator#CONCURRENT},* {@link Spliterator#ORDERED}, and {@link Spliterator#NONNULL}.** @implNote* The {@code Spliterator} implements {@code trySplit} to permit limited* parallelism.** @return a {@code Spliterator} over the elements in this queue* @since 1.8*/public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {return new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.LBQSpliterator<E>(this);}/*** Saves this queue to a stream (that is, serializes it).** @param s the stream* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs* @serialData The capacity is emitted (int), followed by all of* its elements (each an {@code Object}) in the proper order,* followed by a null*/private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)throws java.io.IOException {fullyLock();try {// Write out any hidden stuff, plus capacitys.defaultWriteObject();// Write out all elements in the proper order.for (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next)s.writeObject(p.item);// Use trailing null as sentinels.writeObject(null);} finally {fullyUnlock();}}/*** Reconstitutes this queue from a stream (that is, deserializes it).* @param s the stream* @throws ClassNotFoundException if the class of a serialized object* could not be found* @throws java.io.IOException if an I/O error occurs*/private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {// Read in capacity, and any hidden stuffs.defaultReadObject();count.set(0);last = head = new ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue.Node<E>(null);// Read in all elements and place in queuefor (;;) {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E item = (E)s.readObject();if (item == null)break;add(item);}}public int getCapacity() {return capacity;}public void setCapacity(int capacity) {this.capacity = capacity;}
}
controller接口
提供查询线程池状态,修改线程池参数方法, 以及测试线程池方法
import com.example.redissiontest.config.ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;/*** desc: 测试动态配置线程池** @author qts* @date 2023/11/15 0015*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/threadpool")
@Slf4j
public class ThreadPoolTestController {@Autowiredprivate ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor;// 业务操作@GetMapping("/biz")public String test(@RequestParam Integer concurrencyCount) {for (int i = 0; i < concurrencyCount; i++) {final int index = i + 1;try {threadPoolExecutor.execute(() -> {try {Thread.sleep(2000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}printThreadPoolStatus(index);});} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {log.error("biz拒绝-index={}", index);}}return "success";}/**** 打印当前线程池的状态*/public void printThreadPoolStatus(int index) {log.info("biz执行-index={};core_size:{};thread_current_size:{};" +"thread_max_size:{};queue_capacity{};queue_current_size:{}",index, threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize(),threadPoolExecutor.getActiveCount(), threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize(),((ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue)threadPoolExecutor.getQueue()).getCapacity(),threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());}// 查询线程参数@GetMapping("/getParams")public Map<String, Integer> getParams() {HashMap<String, Integer> params = new LinkedHashMap<>();params.put("core_size", threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());params.put("thread_max_size", threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());params.put("queue_capacity",((ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue)threadPoolExecutor.getQueue()).getCapacity());params.put("thread_current_size",threadPoolExecutor.getActiveCount());params.put("queue_current_size", threadPoolExecutor.getQueue().size());return params;}// 修改线程参数@PutMapping("/changeParams")public String changeParams(@RequestBody Map<String, Object> params) {ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue queue= (ResizableCapacityLinkedBlockingQueue)threadPoolExecutor.getQueue();log.info("corePoolSize before => {}", threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());log.info("maxPoolSize before => {}", threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());log.info("queueCapacity before => {}", queue.getCapacity());threadPoolExecutor.setCorePoolSize((Integer) params.get("corePoolSize"));threadPoolExecutor.setMaximumPoolSize((Integer) params.get("maxPoolSize"));queue.setCapacity((Integer) params.get("queueCapacity"));log.info("corePoolSize after => {}", threadPoolExecutor.getCorePoolSize());log.info("maxPoolSize after => {}", threadPoolExecutor.getMaximumPoolSize());log.info("queueCapacity before => {}", queue.getCapacity());return "success";}
}
测试结果
- 初始参数: corePoolSize=2,maxPoolSize=4,queueCapacity=10
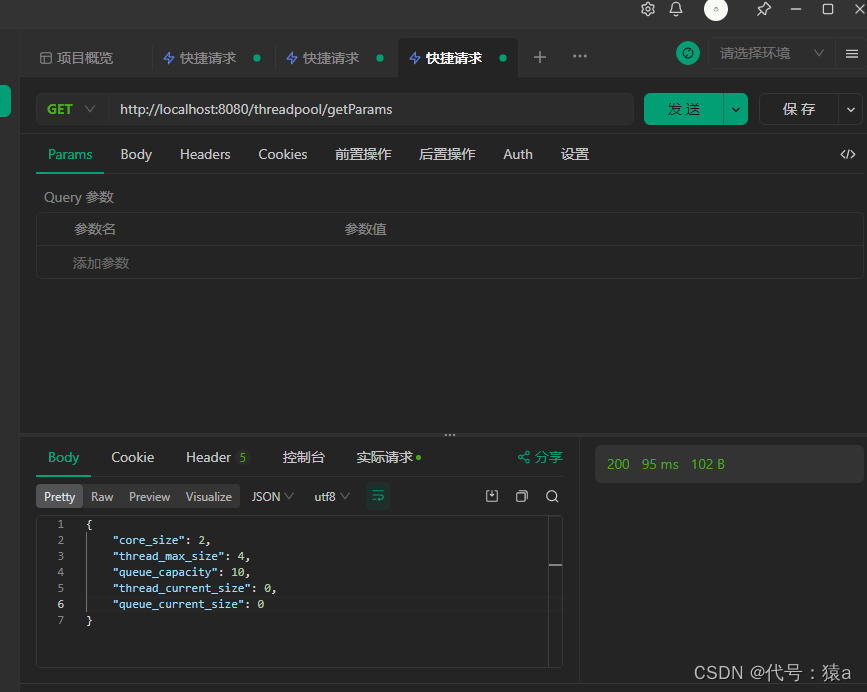
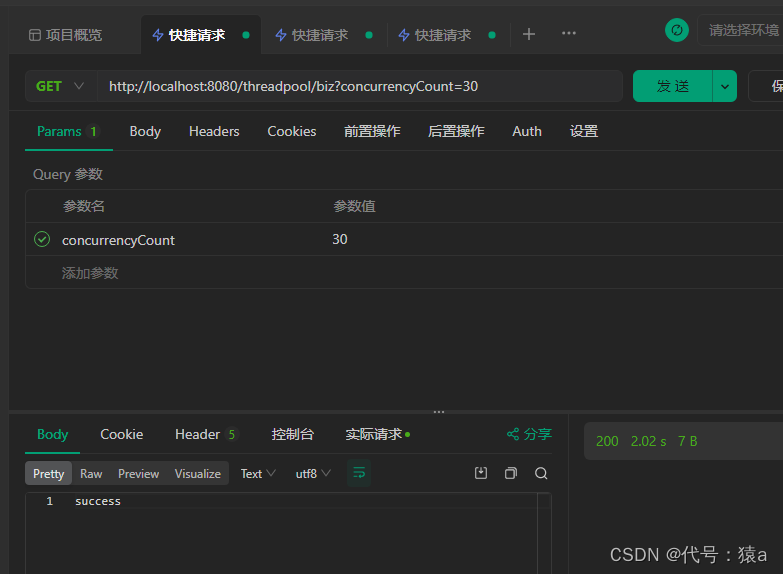
- 执行测试方法,并发量30
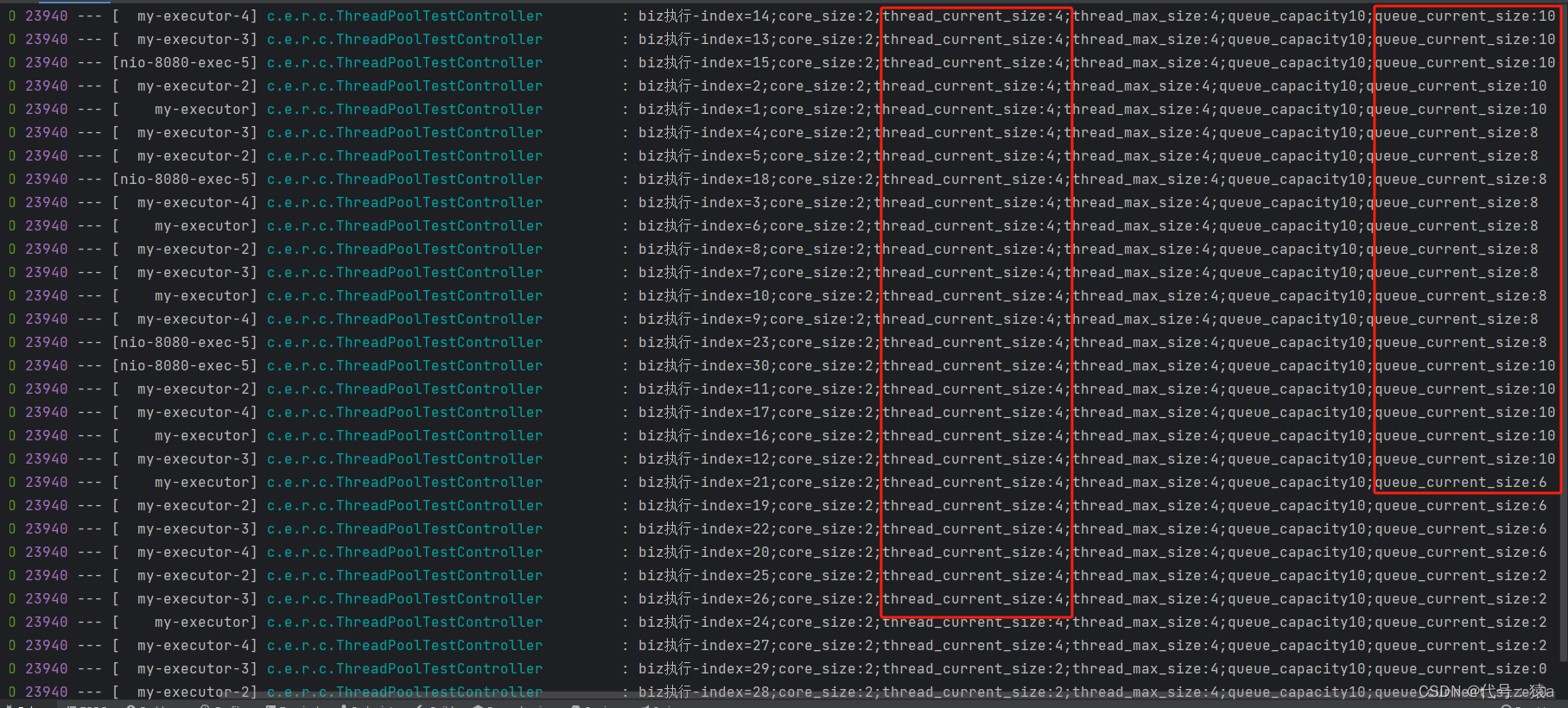
- 测试接口控制台, 当前线程数最多4个,当前队列数量最多10个任务等待
- 修改测试 corePoolSize=3, maxPoolSize=6,queueCapacity=20
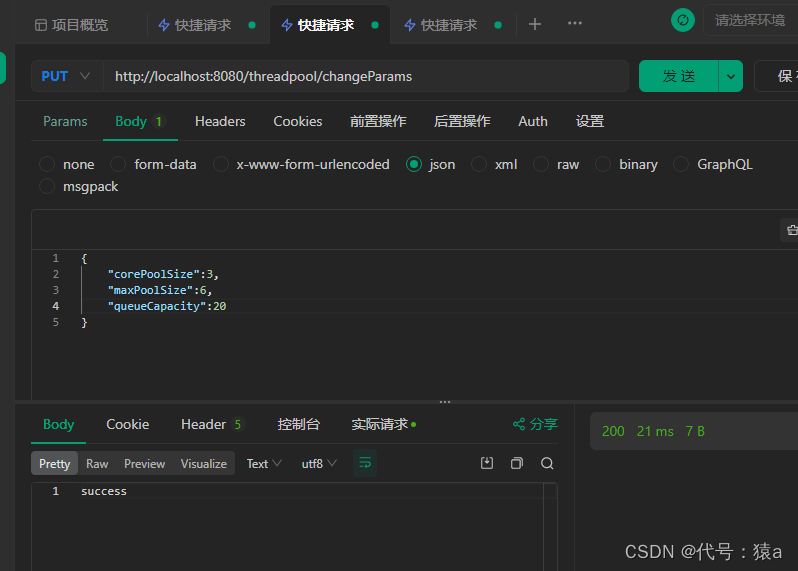
- 查询线程池状态,发生变化
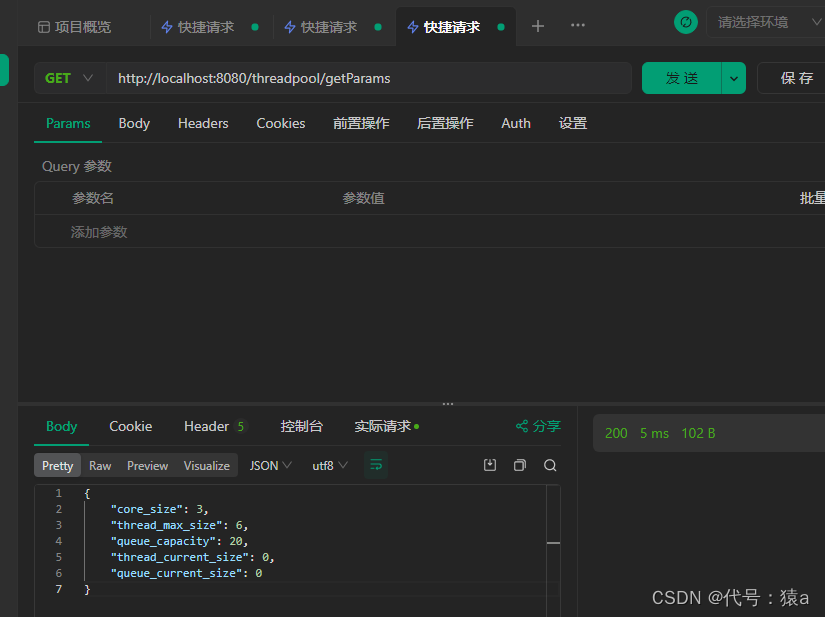
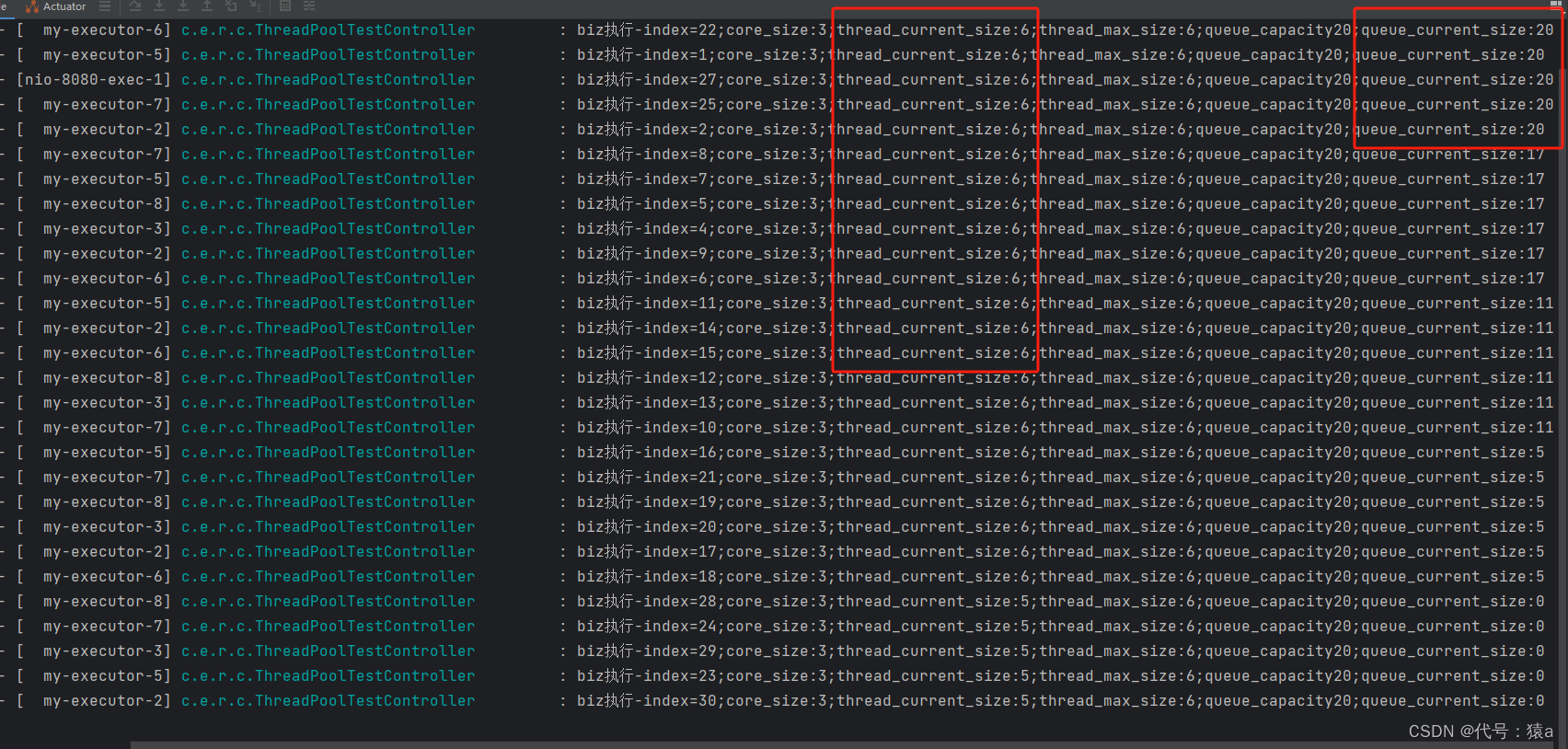
- 再执行测试接口,并发量30 , 观察当前线程数是否是6, 及当前队列的任务数量是否最大是20 , 是则代表动态设置成功
参考文章 文章1
参考文章 文章2
