建站公司可靠吗百度系app
1 为什么用文件锁
文件是一种共享资源,多个进程对同一文件进行操作的时候,必然涉及到竞争状态,因此引入了文件锁实现对共享资源的访问进行保护的机制,通过对文件上锁, 来避免访问共享资源产生竞争状态。
2 文件锁用法
(1)参考文档:
man 2 fcntl
(2)头文件:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
(3)函数定义:
int fcntl(int fd, int cmd, … /* arg */ );
(4)参数:
cmd 取值:
F_GETLK 获取锁
F_SETLK 设置锁
F_SETLKW 同步设置锁
(5)文件锁struct flock的定义:
struct flock {short l_type; //锁的类型(F_RDLCK(读锁), F_WRLCK(写锁), F_UNLCK (解锁))off_t l_start; //指明文件加锁的开始位置(同l_whence)short l_whence; //标志文件锁的初始位置(SEEK_SET, SEEK_CUR, SEEK_END) off_t l_len; //加锁的长度(字节), 0表示整个文件 pid_t l_pid; //是加锁进程的进程 id。
}
3应用举例
#include<unistd.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>#define FILE_NAME "flock_demo.txt"int flock_set(int fd, int type) {printf("进程pid=%d 来啦!\n",getpid());//创建文件锁struct flock fflock;memset(&fflock,0,sizeof(struct flock));fcntl(fd,F_GETLK,&fflock);//文件已经获过取锁了if (fflock.l_type != F_UNLCK) {//文件已上锁if (fflock.l_type == F_RDLCK) {//文件的上读锁printf("抱歉,进程%d已经加上读锁!\n",fflock.l_pid);}else if(fflock.l_type == F_WRLCK)//文件上写锁{printf("抱歉,进程%d已经加上写锁!\n", fflock.l_pid);} }//配置文件锁fflock.l_type = type; //锁的类型fflock.l_whence = SEEK_SET; //文件头fflock.l_start = 0; //锁字节为单位的偏移fflock.l_len = 0; //锁多长内容(0表示整的文件)fflock.l_pid = -1;if (fcntl(fd,F_SETLKW, &fflock)<0){printf("上锁失败!\n");return -1;}switch (fflock.l_type){case F_RDLCK:printf("进程%d加上读锁成功!\n", getpid());break;case F_WRLCK:printf("进程%d加上写锁成功!\n", getpid());break;case F_UNLCK:printf("进程%d已解锁成功!\n", getpid());break;default:break;}printf("进程pid=%d退出\n",getpid());return 0;
}int main(void) {int fd=0;fd = open(FILE_NAME,O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0666);if (fd<0) {fprintf(stderr,"打开文件%s失败,错误原因%s\n", FILE_NAME,strerror(errno));exit(-1);}flock_set(fd, F_WRLCK); //对打开的文件写锁getchar();flock_set(fd, F_UNLCK); //对打开的文件解锁getchar();close(fd);return 0;
}
运行效果:
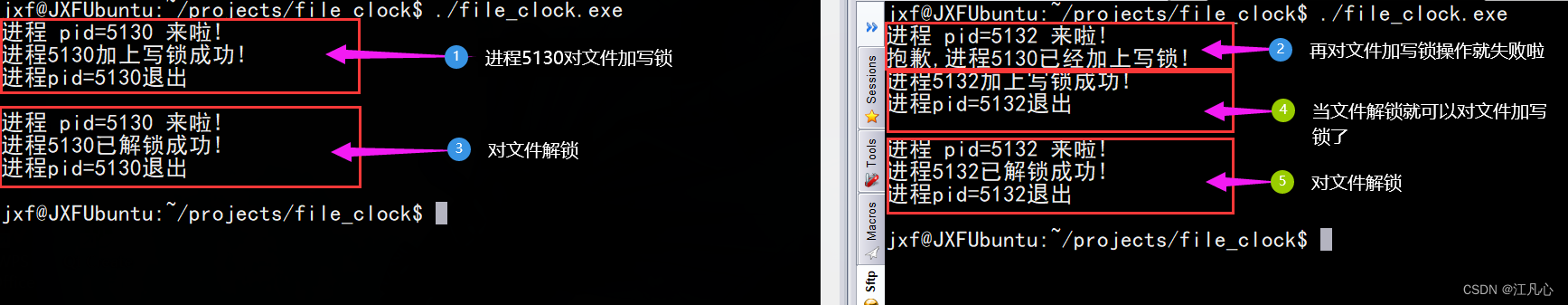
注意:可以同时对文件进行加读锁不受影响,单对文件加写锁则会互斥
