微信投票网站制作凡科官网免费制作小程序
对于神经网络架构的可视化是很有意义的,可以在很大程度上帮助到我们清晰直观地了解到整个架构,我们在前面的 PyTorch的ONNX结合MNIST手写数字数据集的应用(.pth和.onnx的转换与onnx运行时)
有介绍,可以将模型架构文件(常见的格式都可以)在线上传到 https://netron.app/,将会生成架构示意图,比如将yolov5s.pt这个预训练模型,上传之后,将出现下面这样的图片(局部):

这种属于非常简单的层的连接展示,也能够直观知道整个架构是由哪些层组成,虽然每层可以查看一些属性,不过对于每层的具体细节并没有那么直观展现在图片当中。
接下来介绍的这两款都会生成漂亮的可视化神经网络图,可以用来绘制报告和演示使用,效果非常棒。
1、NN-SVG
NN-SVG生成神经网络架构的地址:http://alexlenail.me/NN-SVG/AlexNet.html
显示可能很慢,最好科学上网,进去之后,我们可以看到,有三种神经网络架构可以进行设置:FCNN、LeNet、AlexNet 我们分别来看下:
1.1、FCNN
第一种就是最基础的全连接神经网络FCNN,输入层-->隐藏层(若干)-->输出层,截图如下:

左侧边栏可以进行一些颜色、形状、透明度等设置,也可以很方便的增加和减少层。右边就会实时的显示出操作的效果。
1.2、LeNet
LeNet是一种经典的卷积神经网络,最初用来识别手写数字,我们来看下其结构:

可以看到架构主要是由卷积层组成,输入层-->卷积层-->最大池化层-->...-->全连接层-->输出层。
左边同样的都是可以设置颜色,透明度等,可以增减层数,在每层里可以设置数量、高宽以及卷积核大小,还可以指定是否显示层的名称,这样就更加清楚的知道架构是由哪些具体的层组成了。
1.3、AlexNet
AlexNet是辛顿和他的学生Alex Krizhevsky设计的CNN,在2012年ImageNet的竞赛中获得冠军,它是在LeNet的基础上应用了ReLU激活函数(取代Sigmoid)、Dropout层(避免过拟合)、LRN层(增强泛化能力)等的一种神经网络,截图如下:

同样的可以直观看到,每个层的数量、宽高、卷积核的大小,这些直观的神经网络示意图,尤其对于初学者来说可以很好的理解某个神经网络的整个计算过程。
最后的这些都是可以点击"Download SVG"将其下载成svg格式(一种XML格式)的文件。
2、PlotNeuralNet
2.1、安装
首先确认自己的操作系统,然后对应着进行安装,后面出现的示例是本人的Ubuntu 18.04版本上做的。
Ubuntu 16.04
sudo apt-get install texlive-latex-extraUbuntu 18.04.2
基于本网站,请安装以下软件包,包含一些字体包:
sudo apt-get install texlive-latex-base
sudo apt-get install texlive-fonts-recommended
sudo apt-get install texlive-fonts-extra
sudo apt-get install texlive-latex-extra
Windows或其他系统
下载安装MiKTeX:https://miktex.org/download
下载安装Git bash:https://git-scm.com/download/win
或者Cygwin:https://www.cygwin.com/
准备就绪之后运行即可:
cd pyexamples/
bash ../tikzmake.sh test_simple2.2、克隆运行
上面的Latex安装好了之后,就克隆PlotNeuralNet:
git clone https://github.com/HarisIqbal88/PlotNeuralNet.git我们先来执行自带的一个测试文件
cd pyexamples/
bash ../tikzmake.sh test_simple将生成test_simple.pdf,截图如下:
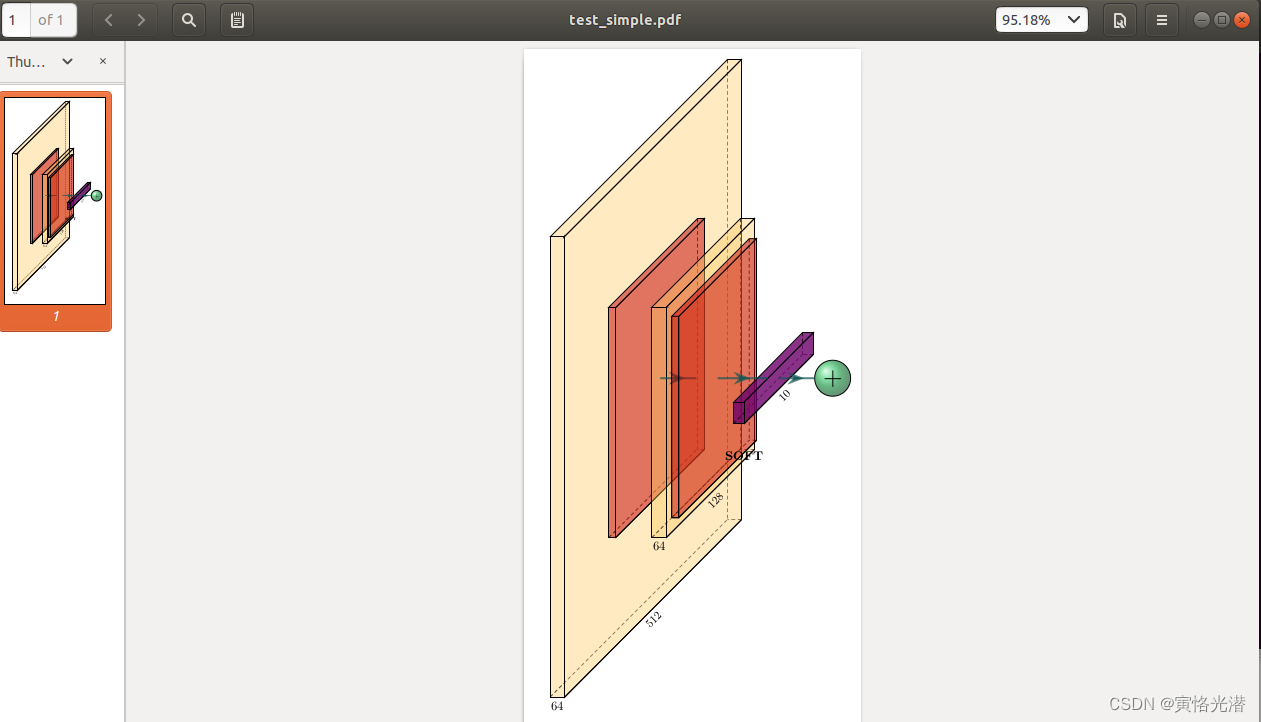
2.3、test_simple.py
我们来看下自带的test_simple.py内容:
import sys
sys.path.append('../')
from pycore.tikzeng import *# defined your arch
arch = [to_head( '..' ),to_cor(),to_begin(),to_Conv("conv1", 512, 64, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", height=64, depth=64, width=2 ),to_Pool("pool1", offset="(0,0,0)", to="(conv1-east)"),to_Conv("conv2", 128, 64, offset="(1,0,0)", to="(pool1-east)", height=32, depth=32, width=2 ),to_connection( "pool1", "conv2"), to_Pool("pool2", offset="(0,0,0)", to="(conv2-east)", height=28, depth=28, width=1),to_SoftMax("soft1", 10 ,"(3,0,0)", "(pool1-east)", caption="SOFT" ),to_connection("pool2", "soft1"), to_Sum("sum1", offset="(1.5,0,0)", to="(soft1-east)", radius=2.5, opacity=0.6),to_connection("soft1", "sum1"),to_end()]def main():namefile = str(sys.argv[0]).split('.')[0]to_generate(arch, namefile + '.tex' )if __name__ == '__main__':main()代码比较简单,导入库之后就是定义架构,然后就自定义的每一层都写在arch这个列表中的 to_begin() 和 to_end() 之间,然后就通过函数 to_generate() 将arch列表生成.tex文件,最后就是通过bash自动转换成pdf文件,我们查看下bash文件内容:cat tikzmake.sh
#!/bin/bashpython $1.py
pdflatex $1.texrm *.aux *.log *.vscodeLog
rm *.texif [[ "$OSTYPE" == "darwin"* ]]; thenopen $1.pdf
elsexdg-open $1.pdf
fi2.4、自定义网络架构
接下来我们自定义一个网络架构测试下,tony.py:
import sys
sys.path.append('../')
from pycore.tikzeng import *# defined your arch
arch = [to_head('..'),to_cor(),to_begin(),to_input('dog.png', width=18, height=14),to_Conv("conv1", 512, 64, offset="(1,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", height=64, depth=64, width=10,caption="Conv1 Layer"),to_Pool("pool1", offset="(0,0,0)", to="(conv1-east)",caption="Pool1 Layer"),to_Conv("conv2", 128, 64, offset="(4,0,0)", to="(pool1-east)", height=32, depth=32, width=5,caption="Conv2 Layer"),to_connection("pool1", "conv2"),to_Pool("pool2", offset="(0,0,0)", to="(conv2-east)", height=28, depth=28, width=1,caption="Pool2 Layer"),to_SoftMax("soft1", 10 ,"(8,0,0)", "(pool1-east)", caption="Softmax Layer"),to_connection("pool2", "soft1"),to_skip(of="pool1",to="pool2",pos=1.25),to_end()]def main():namefile = str(sys.argv[0]).split('.')[0]to_generate(arch, namefile + '.tex' )if __name__ == '__main__':main()其中一些代码的解释:
to_input:可以指定输入图片
to="(conv1-east)":表示当前层在conv1的东边(右边)
to_connection( "pool1", "conv2"):在两者之间画连接线
caption:标题
to_skip:做跳线,其中pos大于1表示向上进行画线,小于1就是向下,这个可以自己进行调试
如果对一些方法不明确其有哪些参数,可以使用帮助:helpto_input(pathfile, to='(-3,0,0)', width=8, height=8, name='temp')
to_SoftMax(name, s_filer=10, offset='(0,0,0)', to='(0,0,0)', width=1.5, height=3, depth=25, opacity=0.8, caption=' ')
当然这里的需要命令行进入到PlotNeuralNet目录,因为需要加载:from pycore.tikzeng import *
其他层需要加入,依葫芦画瓢即可,很简单,比如:
to_UnPool('Unpool', offset="(5,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)",height=64, width=2, depth=64, caption='Unpool'),
to_ConvRes("ConvRes", s_filer=512, n_filer=64, offset="(10,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", height=64, width=2, depth=64, caption='ConvRes'),
to_ConvSoftMax("ConvSoftMax", s_filer=512, offset="(15,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", height=64, width=2, depth=64, caption='ConvSoftMax'),
to_Sum("sum", offset="(5,0,0)", to="(ConvSoftMax-east)", radius=2.5, opacity=0.6),...
2.5、tikzeng.py
我们来查看下tikzeng.py代码:
import osdef to_head( projectpath ):pathlayers = os.path.join( projectpath, 'layers/' ).replace('\\', '/')return r"""
\documentclass[border=8pt, multi, tikz]{standalone}
\usepackage{import}
\subimport{"""+ pathlayers + r"""}{init}
\usetikzlibrary{positioning}
\usetikzlibrary{3d} %for including external image
"""def to_cor():return r"""
\def\ConvColor{rgb:yellow,5;red,2.5;white,5}
\def\ConvReluColor{rgb:yellow,5;red,5;white,5}
\def\PoolColor{rgb:red,1;black,0.3}
\def\UnpoolColor{rgb:blue,2;green,1;black,0.3}
\def\FcColor{rgb:blue,5;red,2.5;white,5}
\def\FcReluColor{rgb:blue,5;red,5;white,4}
\def\SoftmaxColor{rgb:magenta,5;black,7}
\def\SumColor{rgb:blue,5;green,15}
"""def to_begin():return r"""
\newcommand{\copymidarrow}{\tikz \draw[-Stealth,line width=0.8mm,draw={rgb:blue,4;red,1;green,1;black,3}] (-0.3,0) -- ++(0.3,0);}\begin{document}
\begin{tikzpicture}
\tikzstyle{connection}=[ultra thick,every node/.style={sloped,allow upside down},draw=\edgecolor,opacity=0.7]
\tikzstyle{copyconnection}=[ultra thick,every node/.style={sloped,allow upside down},draw={rgb:blue,4;red,1;green,1;black,3},opacity=0.7]
"""# layers definitiondef to_input( pathfile, to='(-3,0,0)', width=8, height=8, name="temp" ):return r"""
\node[canvas is zy plane at x=0] (""" + name + """) at """+ to +""" {\includegraphics[width="""+ str(width)+"cm"+""",height="""+ str(height)+"cm"+"""]{"""+ pathfile +"""}};
"""# Conv
def to_Conv( name, s_filer=256, n_filer=64, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=1, height=40, depth=40, caption=" " ):return r"""
\pic[shift={"""+ offset +"""}] at """+ to +""" {Box={name=""" + name +""",caption="""+ caption +r""",xlabel={{"""+ str(n_filer) +""", }},zlabel="""+ str(s_filer) +""",fill=\ConvColor,height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""# Conv,Conv,relu
# Bottleneck
def to_ConvConvRelu( name, s_filer=256, n_filer=(64,64), offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=(2,2), height=40, depth=40, caption=" " ):return r"""
\pic[shift={ """+ offset +""" }] at """+ to +""" {RightBandedBox={name="""+ name +""",caption="""+ caption +""",xlabel={{ """+ str(n_filer[0]) +""", """+ str(n_filer[1]) +""" }},zlabel="""+ str(s_filer) +""",fill=\ConvColor,bandfill=\ConvReluColor,height="""+ str(height) +""",width={ """+ str(width[0]) +""" , """+ str(width[1]) +""" },depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""# Pool
def to_Pool(name, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=1, height=32, depth=32, opacity=0.5, caption=" "):return r"""
\pic[shift={ """+ offset +""" }] at """+ to +""" {Box={name="""+name+""",caption="""+ caption +r""",fill=\PoolColor,opacity="""+ str(opacity) +""",height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""# unpool4,
def to_UnPool(name, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=1, height=32, depth=32, opacity=0.5, caption=" "):return r"""
\pic[shift={ """+ offset +""" }] at """+ to +""" {Box={name="""+ name +r""",caption="""+ caption +r""",fill=\UnpoolColor,opacity="""+ str(opacity) +""",height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""def to_ConvRes( name, s_filer=256, n_filer=64, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=6, height=40, depth=40, opacity=0.2, caption=" " ):return r"""
\pic[shift={ """+ offset +""" }] at """+ to +""" {RightBandedBox={name="""+ name + """,caption="""+ caption + """,xlabel={{ """+ str(n_filer) + """, }},zlabel="""+ str(s_filer) +r""",fill={rgb:white,1;black,3},bandfill={rgb:white,1;black,2},opacity="""+ str(opacity) +""",height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""# ConvSoftMax
def to_ConvSoftMax( name, s_filer=40, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=1, height=40, depth=40, caption=" " ):return r"""
\pic[shift={"""+ offset +"""}] at """+ to +""" {Box={name=""" + name +""",caption="""+ caption +""",zlabel="""+ str(s_filer) +""",fill=\SoftmaxColor,height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""# SoftMax
def to_SoftMax( name, s_filer=10, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", width=1.5, height=3, depth=25, opacity=0.8, caption=" " ):return r"""
\pic[shift={"""+ offset +"""}] at """+ to +""" {Box={name=""" + name +""",caption="""+ caption +""",xlabel={{" ","dummy"}},zlabel="""+ str(s_filer) +""",fill=\SoftmaxColor,opacity="""+ str(opacity) +""",height="""+ str(height) +""",width="""+ str(width) +""",depth="""+ str(depth) +"""}};
"""def to_Sum( name, offset="(0,0,0)", to="(0,0,0)", radius=2.5, opacity=0.6):return r"""
\pic[shift={"""+ offset +"""}] at """+ to +""" {Ball={name=""" + name +""",fill=\SumColor,opacity="""+ str(opacity) +""",radius="""+ str(radius) +""",logo=$+$}};
"""def to_connection( of, to):return r"""
\draw [connection] ("""+of+"""-east) -- node {\midarrow} ("""+to+"""-west);
"""def to_skip( of, to, pos=1.25):return r"""
\path ("""+ of +"""-southeast) -- ("""+ of +"""-northeast) coordinate[pos="""+ str(pos) +"""] ("""+ of +"""-top) ;
\path ("""+ to +"""-south) -- ("""+ to +"""-north) coordinate[pos="""+ str(pos) +"""] ("""+ to +"""-top) ;
\draw [copyconnection] ("""+of+"""-northeast)
-- node {\copymidarrow}("""+of+"""-top)
-- node {\copymidarrow}("""+to+"""-top)
-- node {\copymidarrow} ("""+to+"""-north);
"""def to_end():return r"""
\end{tikzpicture}
\end{document}
"""def to_generate( arch, pathname="file.tex" ):with open(pathname, "w") as f: for c in arch:print(c)f.write( c )从这些代码也可以看出,通过这些方法,返回的是Latex代码来进行绘制的。
运行命令:bash ../tikzmake.sh tony 生成如图:

可以看到生成的可视化架构图,相比较于以前手工做图来说,真的大大提高了效率。更多详情可以去看具体源码。
github:PlotNeuralNet
