武汉网络兼职网站建设网站页面怎么优化
前言
通过一个简单的自定义的监听器,从源码的角度分一下Spring中监听的整个过程,分析监听的作用。
一、自定义监听案例
1.1定义事件
package com.lazy.snail;import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent;/*** @ClassName UserRegisteredEvent* @Description TODO* @Author lazysnail* @Date 2024/11/8 10:37* @Version 1.0*/
@Getter
public class UserRegisteredEvent extends ApplicationEvent {private final String username;public UserRegisteredEvent(Object source, String username) {super(source);this.username = username;}
}
1.2定义监听
package com.lazy.snail;import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;/*** @ClassName UserRegisteredListener* @Description TODO* @Author lazysnail* @Date 2024/11/8 10:36* @Version 1.0*/
@Component
public class UserRegisteredListener {@EventListenerpublic void handleUserRegisterEvent(UserRegisteredEvent event) {System.out.println("用户注册成功,发送邮件通知");}
}
1.3定义用户服务(发布事件)
package com.lazy.snail;import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisher;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/*** @ClassName UserService* @Description TODO* @Author lazysnail* @Date 2024/11/8 10:37* @Version 1.0*/
@Service
public class UserService {private final ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;public UserService(ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher) {this.eventPublisher = eventPublisher;}public void registerUser(String username) {// 用户注册逻辑System.out.println("Registering user: " + username);// 发布用户注册事件eventPublisher.publishEvent(new UserRegisteredEvent(this, username));}
}
1.4测试类
package com.lazy.snail;import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;@Slf4j
public class SpringTest {@Testvoid test() {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);context.getBean(UserService.class).registerUser("lazysnail");}
}
1.5测试结果

二、事件监听流程
2.1容器启动阶段
2.1.1事件监听方法处理器及默认事件监听工厂
- 事件监听方法处理器及默认事件监听工厂的bean定义信息注册
- 事件监听方法处理器会在后续用于处理自定义监听中的@EventListener注解
- 默认事件监听工厂会用于将自定义监听封装为ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {// 省略部分代码...// 事件监听方法处理器if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));}// 默认事件监听工厂if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);def.setSource(source);beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));}return beanDefs;
}
- 事件监听方法处理器及默认事件监听工厂的实例化
- refresh方法中,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors处理BeanFactoryPostProcessor(EventListenerMethodProcessor实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor)
- 实例化EventListenerMethodProcessor
- 调用EventListenerMethodProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory实例化DefaultEventListenerFactory

// EventListenerMethodProcessor
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {this.beanFactory = beanFactory;Map<String, EventListenerFactory> beans = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(EventListenerFactory.class, false, false);List<EventListenerFactory> factories = new ArrayList<>(beans.values());AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(factories);this.eventListenerFactories = factories;
}
2.1.3应用事件广播器创建
- 容器刷新时,initApplicationEventMulticaster创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
- 注册单例到容器
// AbstractApplicationContext
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {// 为容器初始化事件广播器initApplicationEventMulticaster();
}
// AbstractApplicationContext
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " +"[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]");}
}
- SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster从AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster继承过来一个defaultRetriever对象
- defaultRetriever中封装了监听器集合
private class DefaultListenerRetriever {public final Set<ApplicationListener<?>> applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>();public final Set<String> applicationListenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
- 监听集合中的监听是何时添加的
提前实例化单例后EventListenerMethodProcessor对容器中所有监听处理时添加
// DefaultListableBeanFactory
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {// 省略部分代码...// EventListenerMethodProcessorfor (String beanName : beanNames) {Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {StartupStep smartInitialize = this.getApplicationStartup().start("spring.beans.smart-initialize").tag("beanName", beanName);SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();return null;}, getAccessControlContext());} else {// 单例实例化后处理smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();}smartInitialize.end();}}
}
- 监听器的创建
// EventListenerMethodProcessor
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.beanFactory;Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No ConfigurableListableBeanFactory set");String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class);// 处理UserRegisteredListenerfor (String beanName : beanNames) {// 省略部分代码...processBean(beanName, type);}
}private void processBean(final String beanName, final Class<?> targetType) {if (!this.nonAnnotatedClasses.contains(targetType) &&AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(targetType, EventListener.class) &&!isSpringContainerClass(targetType)) {Map<Method, EventListener> annotatedMethods = null;// 省略部分代码...// @EventListener注解的方法(注解上的属性)annotatedMethods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(targetType,(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<EventListener>) method ->AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(method, EventListener.class));if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(annotatedMethods)) {this.nonAnnotatedClasses.add(targetType);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("No @EventListener annotations found on bean class: " + targetType.getName());}} else {// Non-empty set of methodsConfigurableApplicationContext context = this.applicationContext;Assert.state(context != null, "No ApplicationContext set");List<EventListenerFactory> factories = this.eventListenerFactories;Assert.state(factories != null, "EventListenerFactory List not initialized");for (Method method : annotatedMethods.keySet()) {for (EventListenerFactory factory : factories) {if (factory.supportsMethod(method)) {Method methodToUse = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, context.getType(beanName));// 事件监听工厂创建应用监听器 ApplicationListenerMethodAdapterApplicationListener<?> applicationListener =factory.createApplicationListener(beanName, targetType, methodToUse);if (applicationListener instanceof ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) {((ApplicationListenerMethodAdapter) applicationListener).init(context, this.evaluator);}// 添加到应用上下文context.addApplicationListener(applicationListener);break;}}}}}
}
2.2客户端调用阶段
- 发布事件
// AbstractApplicationContext
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);
}
-
拿到内部应用事件广播器(SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster)
-
广播器广播事件
// SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster
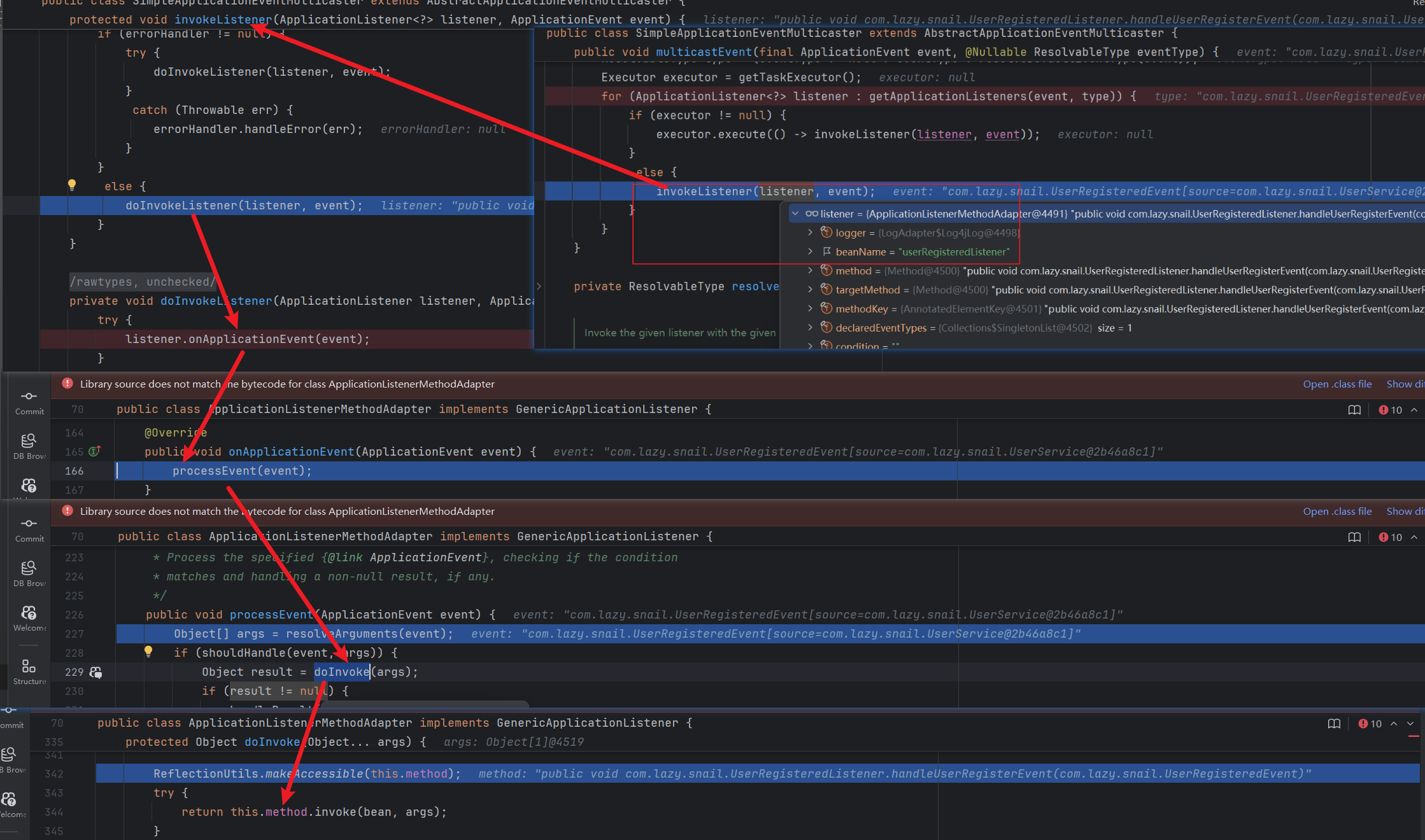
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {if (executor != null) {executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));} else {invokeListener(listener, event);}}
}
- 获取监听
- 检索应用监听器
- 直接从检索器(defaultRetriever)中取出监听
/*** 根据给定的事件、源(我理解是容器)检索监听器* */
// AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster
private Collection<ApplicationListener<?>> retrieveApplicationListeners(ResolvableType eventType, @Nullable Class<?> sourceType, @Nullable CachedListenerRetriever retriever) {List<ApplicationListener<?>> allListeners = new ArrayList<>();Set<ApplicationListener<?>> filteredListeners = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);Set<String> filteredListenerBeans = (retriever != null ? new LinkedHashSet<>() : null);Set<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners;Set<String> listenerBeans;synchronized (this.defaultRetriever) {// 默认检索器中获取应用监听,监听已经在Spring启动阶段注册完成listeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners);listenerBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.defaultRetriever.applicationListenerBeans);}// 省略部分代码...AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(allListeners);if (retriever != null) {if (filteredListenerBeans.isEmpty()) {retriever.applicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(allListeners);retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;}else {retriever.applicationListeners = filteredListeners;retriever.applicationListenerBeans = filteredListenerBeans;}}return allListeners;
}
- 调用监听
invokeListener
三、总结
- 个人理解:
事件发布是一个抽象的概念,真正将事件发布出去的是SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster,发布事件实际做的事情,找到监听器,过滤出能够处理这个事件的监听器,然后执行监听器中针对这个事件的业务逻辑。
3.1监听流程总结
3.1.1. Spring 容器启动
- 在 Spring 启动过程中,
ApplicationContext被初始化,它作为核心容器,提供了事件发布和监听的机制。 - Spring 使用
ApplicationEventPublisher作为事件发布的核心接口,事件的发布与处理都在ApplicationContext内部实现。
3.1.2. 监听器注册
- 在 Spring 中,可以通过以下几种方式注册监听器:
- 实现
ApplicationListener接口:将实现类作为 Spring Bean 注册,Spring 会自动将它识别为事件监听器。 - 通过 XML 配置:在 XML 文件中配置
<bean class="com.example.MyEventListener"/>,将监听器注册到ApplicationContext。 - 注解方式:使用@EventListener注解
- 实现
- 监听器的作用:每当发布的事件类型与监听器泛型参数中的事件类型匹配时,监听器的
onApplicationEvent方法就会被调用。
3.1.3. 事件发布
- 发布者:Spring 中的任何组件都可以通过
ApplicationEventPublisher发布事件。通常,ApplicationContext本身实现了ApplicationEventPublisher,可以直接调用publishEvent()发布事件。 - 事件传播器:默认情况下,Spring 使用
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为事件传播器,它负责查找符合条件的监听器并将事件分发给它们。 - 发布事件的方法:通过
applicationContext.publishEvent(new CustomEvent(this))来发布事件。
3.1.4. 事件广播给监听器
- 筛选监听器:
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster会检查所有注册的监听器,筛选出对当前事件感兴趣的监听器(基于事件类型的匹配)。 - 同步与异步:在 Spring 环境中,默认情况下事件是同步传递的,所有监听器在主线程中执行。如果需要异步,可以通过自定义
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster并配置线程池。
3.1.5. 监听器处理事件
- 监听逻辑执行:每个匹配的监听器会调用
onApplicationEvent()方法,执行相应的业务逻辑。 - 异常处理:如果监听器抛出异常,
SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster会捕获并记录日志,但不会影响其他监听器的执行。
3.1.6. 事件传播的扩展
- 在某些场景中,一个事件的监听器可能会发布新的事件,这会形成事件链。Spring 容器会递归地将这些新事件广播给感兴趣的监听器。
3.2应用场景
3.2.1. 解耦业务逻辑
- 场景描述:在业务流程中,常常需要在某个操作完成后执行附加逻辑,比如用户注册后发送欢迎邮件、推送通知、或更新统计数据。
- 实现方式:通过监听器监听用户注册事件,执行后续的附加操作。这样,核心业务逻辑与附加逻辑可以解耦,各自独立管理。
- 示例:用户注册成功后触发
UserRegistrationEvent,监听器接收事件后完成发送邮件或通知的任务。
3.2.2. 事务性事件
- 场景描述:在某些情况下,需要确保只有当事务成功提交后,才会发布事件。比如在订单创建后,确保库存减少或通知支付系统。
- 实现方式:通过
@TransactionalEventListener监听事务性事件,确保事件只有在事务提交成功时才会触发。 - 示例:订单创建完成并且数据库事务成功提交后,触发
OrderCreatedEvent,通知库存系统减少库存。
3.2.3. 异步处理任务
- 场景描述:对于不需要实时完成的任务,可以通过异步监听器来解放主线程,避免阻塞。
- 实现方式:在事件监听器方法上使用
@Async,使其在独立线程中执行异步任务。 - 示例:用户在系统中上传文件,文件处理逻辑通过事件异步执行,以保证上传接口的快速响应。
3.2.4. 应用启动或关闭事件
- 场景描述:在应用启动或关闭时,通常需要执行一些初始化或清理操作,比如加载配置、检查依赖服务、关闭资源等。
- 实现方式:通过监听
ApplicationReadyEvent、ContextClosedEvent等应用上下文事件,实现启动和关闭时的操作。 - 示例:在应用启动完成后加载配置文件,或在应用关闭时清理缓存或关闭数据库连接。
3.2.5. 状态变化或监控
- 场景描述:在系统中监控某些状态的变化,比如监控服务状态、资源使用情况、流量变化等。
- 实现方式:使用自定义事件来捕获和广播状态变化,监听器实时响应状态变化,执行对应操作。
- 示例:当服务发现高负载时,发布
HighLoadEvent,监听器响应并调整系统参数或生成告警。
3.2.6. 领域驱动设计(DDD)中的事件处理
- 场景描述:在领域驱动设计中,事件驱动架构常用于处理不同领域的事件交互,比如订单模块的事件会影响到支付、物流等模块。
- 实现方式:通过领域事件(如订单支付事件、库存更新事件)来实现模块间的松耦合通信,避免模块之间的直接依赖。
- 示例:在电商系统中,用户下单后触发
OrderPlacedEvent,物流模块监听该事件并安排发货。
3.2.7. 跨服务通信
- 场景描述:在微服务架构中,服务之间往往需要基于事件进行异步通信,降低耦合度。
- 实现方式:通过发布事件到消息中间件(如 Kafka、RabbitMQ),各服务监听感兴趣的事件。
- 示例:支付服务完成支付后触发
PaymentCompletedEvent,订单服务监听该事件并更新订单状态。
3.2.8. 监听应用配置变化
- 场景描述:在应用运行期间,可能需要动态刷新配置,比如数据库连接、缓存配置等。
- 实现方式:通过监听配置中心的配置更新事件,触发配置的刷新。
- 示例:当配置中心检测到 Redis 缓存配置更新后触发
CacheConfigUpdateEvent,应用的缓存配置自动刷新。
3.2.9. 处理安全或认证事件
- 场景描述:在用户认证、权限验证等过程中,可以发布事件来处理安全相关操作。
- 实现方式:监听认证成功、认证失败等事件,执行相应的业务逻辑,比如记录日志、锁定账户。
- 示例:用户多次登录失败后触发
AuthenticationFailureEvent,监听器响应后锁定用户账户并生成告警。
